You might not realize it, but anxiety could already be affecting you
Jul 8, 2024
Identifying Anxiety
Many individuals fail to recognize their anxiety, often misinterpreting its symptoms as physical ailments. For example, chest tightness might be mistaken for a heart problem, and frequent urination could be seen as a bladder issue. These symptoms are often related to anxiety, a condition that can be deeply distressing and challenging to manage.

What is Anxiety?
Let us provide an insightful analogy to explain anxiety. Imagine a small animal in a forest sensing danger from a nearby predator. The threat feels immediate and real, prompting an anxious response. This analogy illustrates how anxiety operates in humans, even in the absence of a clear and concrete threat. In modern society, perceived dangers such as health concerns (e.g., fear of contracting COVID-19) or social anxieties (e.g., fear of exclusion) can trigger similar anxious responses. It's not surprising how many anxious thoughts run through our heads every day.
Psychological and Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety manifests through various psychological and physical symptoms. Psychologically, it includes worry, fear, restlessness, and insomnia. The difference between worry and fear are worry is repetitive and uncontrollable concern about potential problems, while fear is an immediate response to a perceived threat. These psychological symptoms can lead to restlessness and insomnia, creating a cycle of anxiety.
Physically, anxiety activates the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in symptoms like a fast heart rate, rapid breathing, reduced gut movement, and sweating. These symptoms are often misinterpreted as a disorder of the sympathetic nervous system, but the root cause is anxiety.
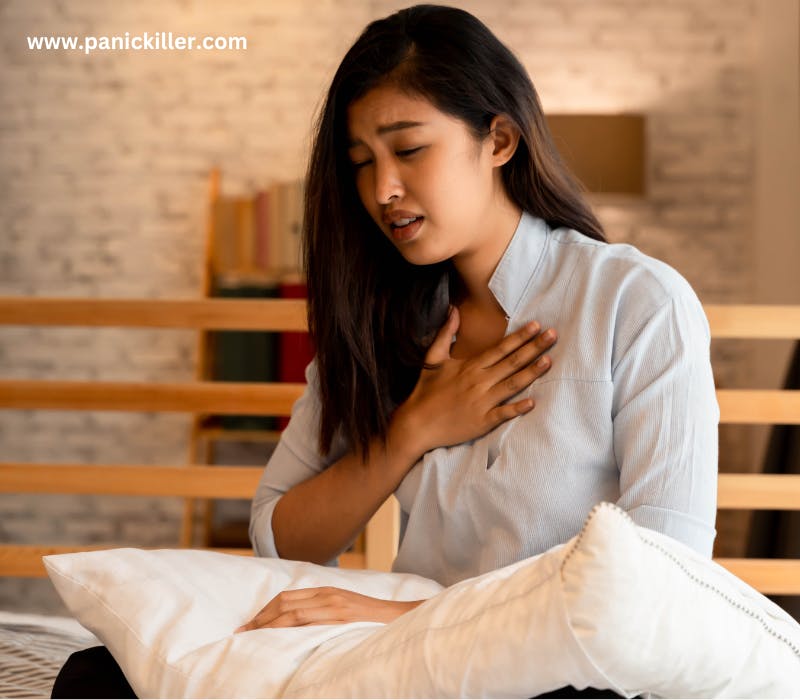

palpitation or chest tightness could be one of the symptoms of anxiety
Neurogenic Inflammation and Anxiety
The brain can cause neurogenic inflammation through the trigeminal nerve, leading to headaches and other physical discomforts. When we get anxious or stressed, the nerve endings release inflammatory substances, signaling the brain's distress. This mechanism underscores the intricate connection between psychological states and physical health.
Common Physical Symptoms of Anxiety
- Muscle Stiffness: Stress and anxiety can cause muscle tension, particularly in the neck, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Trembling: Tense muscles can result in shaking.
- Chest Tightness and Heart Palpitations: The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the heart to beat faster, and breathing quickens to match the heart rate, causing a feeling of breathlessness.
- Digestive Issues: Anxiety can slow down gut movement, leading to poor digestion and constipation. Conversely, some individuals might experience diarrhea and frequent urination due to heightened brain focus on these functions.
- Irregular Breathing: Anxiety can cause hyperventilation, reducing carbon dioxide levels and constricting the brain's blood vessels, leading to dizziness and tingling in the extremities.
- Neurogenic Inflammation: This can cause migraines, neck pain, and a feeling of pressure in the head due to the release of inflammatory substances by nerve endings.
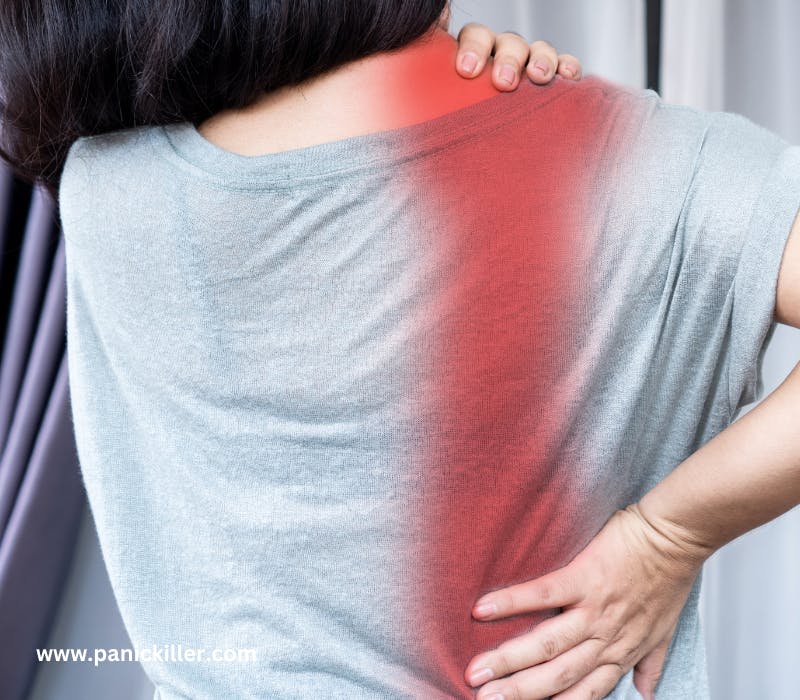
body pain is an example of neurogenic Inflammation
Misinterpretation of Anxiety Symptoms
Some individuals might misinterpret anxiety symptoms as signs of physical illnesses. For example, restlessness might be attributed to being busy, and insomnia to a sleep disorder. Recognizing these symptoms as manifestations of anxiety is crucial for effective treatment.
Case Examples
There are several examples to illustrate how anxiety can manifest in different individuals:
- Young Person on Medication: A young individual taking a common blood pressure medication might experience slight swelling in the extremities, leading to tingling sensations. This can be mistaken for a side effect of the medication, but it might also be a symptom of underlying anxiety.
- Elderly Person with Poor Circulation: An elderly person who remains sedentary might experience poor circulation and mild swelling in their extremities, causing tingling sensations. While this might be attributed to inactivity, it can also be a sign of underlying anxiety.
- Individuals with No Apparent Reason for Anxiety: Even people who seem to have no reason for anxiety—such as those who are retired, financially stable, and have good relationships —can still experience anxiety. For instance, they might feel dizzy without any clear cause. This underscores that anxiety can stem from an unstable brain, even when external conditions appear favorable.
Mechanisms Behind Anxiety Symptoms
Several mechanisms that contribute to the physical symptoms of anxiety:
- Direct Nerve Stimulation: Anxiety can cause direct stimulation of nerves, leading to sensations like tingling in the hands and feet.
- Hyperventilation: When anxious, individuals might breathe too rapidly, leading to hyperventilation. This decreases carbon dioxide levels in the blood, causing the brain's blood vessels to constrict and resulting in dizziness and tingling.
- Neurogenic Inflammation: Anxiety can lead to the release of inflammatory substances by nerve endings, causing sensations like headaches, neck pain, and tingling.
Recognizing and Addressing Anxiety
The first step in managing anxiety is recognizing its presence and understanding its manifestations. Acknowledging these symptoms as signs of anxiety is crucial for effective treatment. Misinterpreting these symptoms as purely physical ailments can delay appropriate interventions and exacerbate the condition.
Conclusion
Anxiety is a multifaceted condition with both psychological and physical manifestations. There are so many various ways anxiety can present itself, often masquerading as physical ailments. Understanding these symptoms as manifestations of anxiety is the first step towards effective management and treatment. By recognizing the underlying causes and addressing them comprehensively, individuals can improve their quality of life and overall well-being.
If you found this discussion insightful, consider sharing it with friends and family. Together, we can improve the awareness and management of anxiety, leading to a healthier and more understanding society. Subscribe to us and learn more about mental health regularly!

Tips for your mental health
Find out more about Anxiety Spiral: Notice the Anxiety Spiral That Might Have Happened to You
Download our panickiller app - The #1 free mobile app to improve mental wellness




